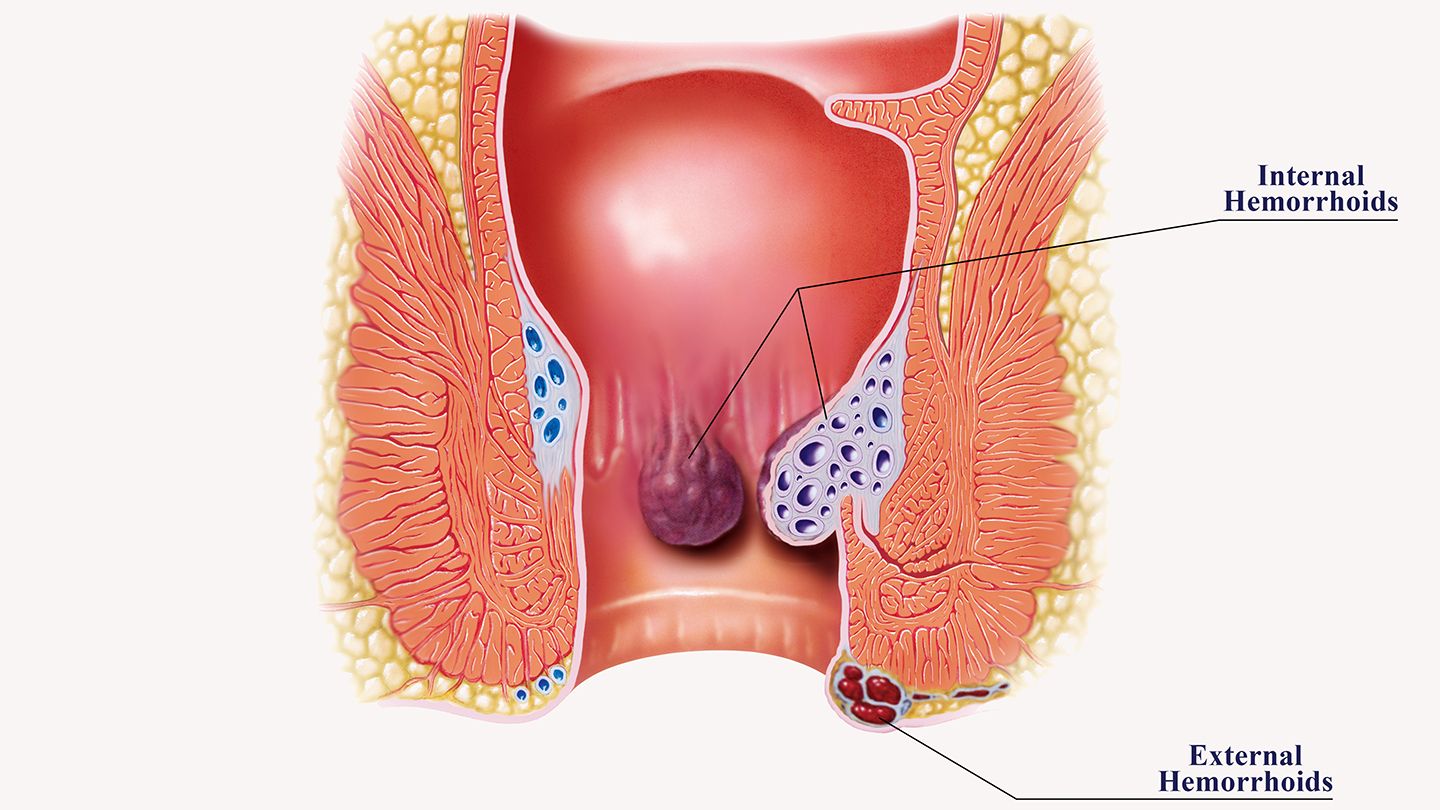
1. Understanding Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins that develop in the anal and rectal area. They can occur both internally and externally. Internal hemorrhoids are located inside the rectum and are typically painless, while external hemorrhoids are visible and can be painful. Hemorrhoids may develop due to various factors, including pregnancy, aging, chronic constipation, and prolonged sitting.
2. Causes of Hemorrhoids
The exact cause of hemorrhoids is not fully understood, but several factors contribute to their development. These include:
-
Pregnancy: The hormonal changes and increased pressure on the veins during pregnancy can lead to the formation of hemorrhoids.
-
Aging: Hemorrhoids are more common among adults over the age of 50, but they can affect people of all ages.
-
Chronic constipation: Straining during bowel movements puts excessive pressure on the blood vessels in the anus and rectum, leading to hemorrhoids.
-
Prolonged sitting: Spending long hours sitting, especially on the toilet, can contribute to the development of hemorrhoids.
-
Low fiber diet: A diet low in fiber can cause constipation, resulting in the formation of hemorrhoids.
-
Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the pressure on the abdomen, leading to hemorrhoids.
-
Genetics: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing hemorrhoids.
3. Symptoms of Hemorrhoids

Hemorrhoids can cause a range of symptoms, which may vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
-
Bleeding during bowel movements
-
Itching or irritation in the anal area
-
Discomfort, pain, or soreness around the anus
-
Swelling or lumps in the anal region
-
Prolapsed hemorrhoids that protrude from the anus
While these symptoms can be uncomfortable, they often improve on their own after a few days. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, medical attention may be necessary.
4. Home Treatments for Hemorrhoids
In many cases, hemorrhoids can be effectively managed at home with simple remedies. Here are some home treatments that can help relieve symptoms:
-
Topical creams and ointments: Over-the-counter creams can reduce itching, discomfort, and swelling associated with external hemorrhoids.
-
Fiber supplements: Taking fiber supplements can help soften the stool and prevent constipation, reducing the strain on hemorrhoids.
-
Ice packs and cold compresses: Applying ice packs to the affected area can help reduce pain and swelling.
-
Sitz baths: Taking warm sitz baths a few times a day can provide relief from hemorrhoid pain.
-
Painkillers: Over-the-counter painkillers like aspirin and ibuprofen can help alleviate pain associated with hemorrhoids.
5. Medications for Hemorrhoids
There are several medications available for the treatment of hemorrhoids. These include:
-
Zinc oxide creams: These creams can help reduce irritation and itching in the anal area.
-
Witch hazel: Astringents like witch hazel can provide temporary relief from hemorrhoid symptoms.
-
Steroid creams: Corticosteroid creams can reduce inflammation in hemorrhoids, but prolonged use should be avoided to prevent skin damage.
-
Lidocaine-based creams: Creams or suppositories containing lidocaine can help alleviate pain and itching.
It is important to consult a doctor before using any medication and to follow the recommended dosage and guidelines.
6. Nonsurgical Treatment Options

If home remedies do not provide sufficient relief, nonsurgical treatment options may be recommended. These include:
-
Rubber band ligation: In this procedure, an elastic band is placed around the base of the hemorrhoid to cut off its blood supply, causing it to shrink and fall off.
-
Sclerotherapy: Doctors inject a liquid into the hemorrhoid to create scar tissue, which blocks the blood supply and reduces its size.
-
Infrared photocoagulation: Infrared light is used to heat the internal hemorrhoid, causing scar tissue to form and shrink the hemorrhoid.
-
Electrocoagulation: Low electric current is applied to the hemorrhoid to create scarring and shrink the hemorrhoid.
These procedures are typically performed on an outpatient basis and under local anesthesia.
7. Surgical Options for Hemorrhoids
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to treat severe or recurring hemorrhoids. Surgical options include:
-
Hemorrhoidectomy: This procedure involves the complete removal of external hemorrhoids or prolapsed internal hemorrhoids.
-
Stapled hemorrhoidopexy: In this procedure, a surgeon staples the prolapsed hemorrhoid back into its normal position in the anus.
Surgical procedures for hemorrhoids are usually performed under general anesthesia, and most patients can go home on the same day as the surgery.
8. Different Types of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids can be classified into different types based on their location and severity. The classification system helps healthcare professionals determine the appropriate treatment approach. The types of hemorrhoids include:
-
Grade 1: Internal hemorrhoids that remain in the rectum without prolapsing.
-
Grade 2: Internal hemorrhoids that prolapse during bowel movements but return inside on their own.
-
Grade 3: Prolapsed internal hemorrhoids that require manual pushing to be repositioned.
-
Grade 4: Prolapsed internal hemorrhoids that cannot be manually repositioned.
The classification of hemorrhoids helps in determining the appropriate treatment approach.
9. Diagnosing Hemorrhoids
To diagnose hemorrhoids, a healthcare professional will typically perform a physical examination and ask about the patient’s medical history. The examination may involve:
-
Visual inspection: The doctor will examine the anal area for external hemorrhoids, lumps, tears, and irritated skin.
-
Digital rectal exam: The doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to check for internal hemorrhoids, blood, sensitivity, and lumps.
-
Anoscope examination: A small device called an anoscope may be used to visualize internal hemorrhoids and assess their severity.
In some cases, further diagnostic tests may be required to rule out other conditions or confirm the diagnosis.
10. Preventing Hemorrhoids
While hemorrhoids may not be entirely preventable, certain lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of developing them. Here are some preventive measures:
-
Eating a healthy diet: Consuming a diet rich in fiber, including fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation.
-
Avoiding straining: Straining during bowel movements should be avoided, as it puts excessive pressure on the veins in the rectum.
-
Prompt bathroom visits: It is important to respond to the body’s natural urge to have a bowel movement and avoid delaying bathroom visits.
-
Regular physical activity: Engaging in regular exercise can promote healthy bowel movements and prevent constipation.
-
Maintaining a moderate body weight: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain on the abdomen and lowers the risk of hemorrhoids.
By implementing these preventive measures, individuals can reduce the likelihood of developing hemorrhoids.
11. Potential Complications

Although hemorrhoids are generally benign, there are potential complications that can arise. These include:
-
Bleeding: Persistent or heavy bleeding from hemorrhoids may indicate the need for medical attention.
-
Strangulated hemorrhoid: In some cases, the muscles around the anus can block the blood supply to a prolapsed hemorrhoid, leading to severe pain.
-
Anemia: Chronic blood loss from hemorrhoids can result in anemia, which occurs when there is a deficiency of red blood cells in the body.
-
Blood clots: Blood clots can sometimes form within external hemorrhoids, causing significant pain. In such cases, a surgeon may need to remove the clot.
-
Infection: Ulceration and infection can occur after certain hemorrhoid treatments.
-
Urinary retention: Surgery for hemorrhoids can sometimes lead to difficulty in passing urine.
If any of these complications arise or if symptoms persist or worsen, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
12. When to Seek Medical Help
In most cases, hemorrhoids can be managed with home treatments and lifestyle changes. However, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional if:
-
Symptoms do not improve after a week of home treatment
-
New hemorrhoids continue to form
-
There is significant anal pain or heavy rectal bleeding
-
Fever is present
These symptoms may indicate the need for medical intervention or further evaluation to rule out other underlying conditions.
In conclusion, hemorrhoids are a common condition that can cause discomfort and pain. However, with proper understanding, home treatments, and medical interventions when necessary, individuals can effectively manage hemorrhoids and prevent complications. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and seeking timely medical attention, individuals can improve their quality of life and minimize the impact of hemorrhoids.
Remember, if you have any concerns or questions about hemorrhoids, it is always best to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment.