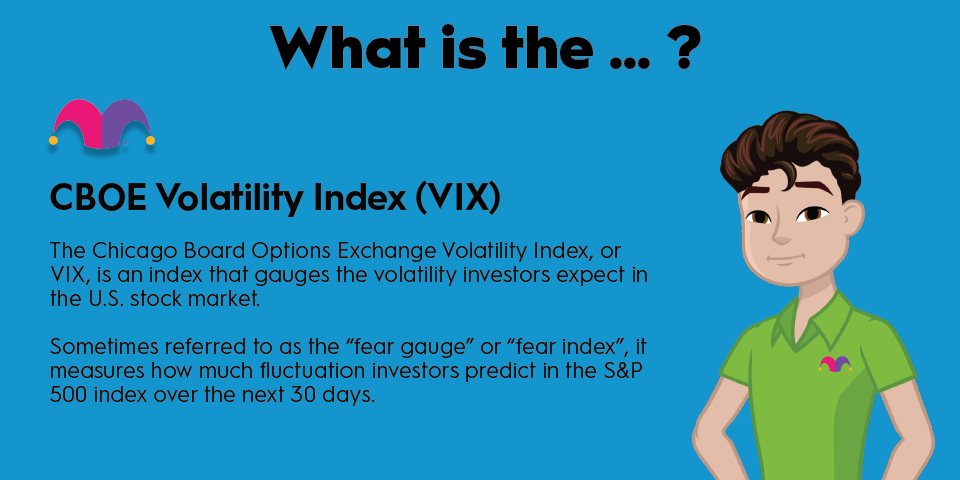
The CBOE Volatility Index (VIX) is a real-time market index that represents the market’s expectations for volatility over the next 30 days. It is often referred to as the “Fear Index” because it measures the level of fear, risk, and stress in the market. The VIX is derived from the prices of S&P 500 index options with near-term expiration dates, which allows it to generate a forward projection of volatility.
Understanding Volatility and Market Sentiment
Volatility refers to how fast prices change in the market. It is an important factor to consider when making investment decisions because it reflects market sentiment and the degree of fear among market participants. The VIX provides a quantifiable measure of market risk and investors’ sentiments, making it a valuable tool for traders and investors.

The Calculation of the VIX
The VIX calculates volatility using two different methods: historical volatility and implied volatility. Historical volatility is based on statistical calculations using past price data, while implied volatility infers its value from options prices. Options are derivative instruments that depend on the probability of a stock’s price reaching a particular level within a specific timeframe.
The VIX uses the second method, which involves deriving implied volatility from market prices of options. This forward-looking implied volatility is an essential input parameter in option pricing models like the Black-Scholes model. By aggregating the weighted prices of multiple S&P 500 index options, the VIX estimates the expected volatility of the index.
Evolution of the VIX
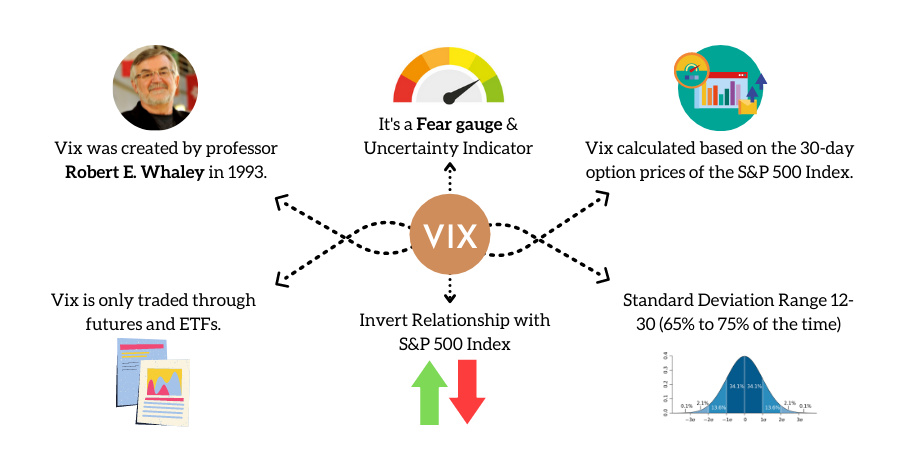
The VIX was introduced in 1993 by the CBOE Options Exchange as a benchmark index to measure the market’s expectation of future volatility. Initially, it was calculated as a weighted measure of the implied volatility of eight S&P 100 at-the-money put and call options. As the derivatives market matured, the methodology was updated in 2003 to include a wider set of options based on the broader S&P 500 Index.
Today, the VIX is an established and globally recognized gauge of U.S. equity market volatility. It is calculated in real-time based on the live prices of the S&P 500 Index. The CBOE disseminates VIX values from 3 a.m. to 9:15 a.m. and from 9:30 a.m. to 4:15 p.m. EST.
Interpreting the VIX Values
The VIX and S&P 500 price volatility tend to exhibit inverse price action. When the stock market falls sharply, the VIX rises, indicating increased fear and uncertainty among investors. Conversely, when the market advances, the VIX values, fear, and volatility decline.
A VIX value above 30 is generally associated with high volatility and increased uncertainty in the market. It suggests a higher level of fear and risk among investors. On the other hand, VIX values below 20 indicate stable and relatively stress-free periods in the market.
Trading the VIX
The VIX has paved the way for using volatility as a tradable asset through derivative products. The CBOE launched the first VIX-based exchange-traded futures contract in 2004, followed by the introduction of VIX options in 2006. These VIX-linked instruments allow investors to gain pure volatility exposure and create a new asset class.
Active traders, institutional investors, and hedge fund managers use VIX-linked securities for portfolio diversification. Historical data shows a strong negative correlation between volatility and stock market returns. When stock returns decline, volatility tends to rise, and vice versa. By incorporating VIX values into their trading strategies, traders can accurately price derivatives based on high beta stocks.
Additionally, the CBOE offers several other variants for measuring broad market volatility, such as the CBOE Short-Term Volatility Index (VIX9D), the CBOE S&P 500 3-Month Volatility Index (VIX3M), and the CBOE S&P 500 6-Month Volatility Index (VIX6M). These indexes provide additional options and futures for trading on CBOE and CFE platforms.
Using the VIX to Hedge Downside Risk
Investors can use the VIX to hedge downside risk by buying put options. Put options increase in value as volatility rises, providing protection against market declines. Astute investors tend to buy put options when the VIX is relatively low and put premiums are cheap. By purchasing protective puts, investors can mitigate potential losses during market downturns.
Impact of the VIX on Option Premiums and Prices
Volatility, as measured by the VIX, has a significant impact on stock and index options’ prices and premiums. Higher VIX values lead to higher option prices, as increased volatility increases the likelihood of larger price swings. Conversely, lower VIX values result in lower option prices or cheaper premiums.
The Normal Range for the VIX
The long-term average of the VIX is around 21. VIX values above 30 indicate high volatility and increased fear and uncertainty in the market. Conversely, VIX values below 20 suggest stable and relatively stress-free periods in the market.
Conclusion
The CBOE Volatility Index (VIX) is a real-time market index that measures the market’s expectations for volatility over the next 30 days. It provides valuable insights into market sentiment, fear, and risk, making it an essential tool for traders and investors. By understanding how the VIX is calculated and how it can be used to hedge downside risk, investors can make more informed investment decisions.