Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the world we live in. This cutting-edge technology, also known as machine intelligence, encompasses various software and hardware components that have the ability to learn, make decisions, and perform actions independently. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different facets of AI, its applications in business, the types of AI, the distinction between AI and machine learning, and the evolving stages of artificial intelligence.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence
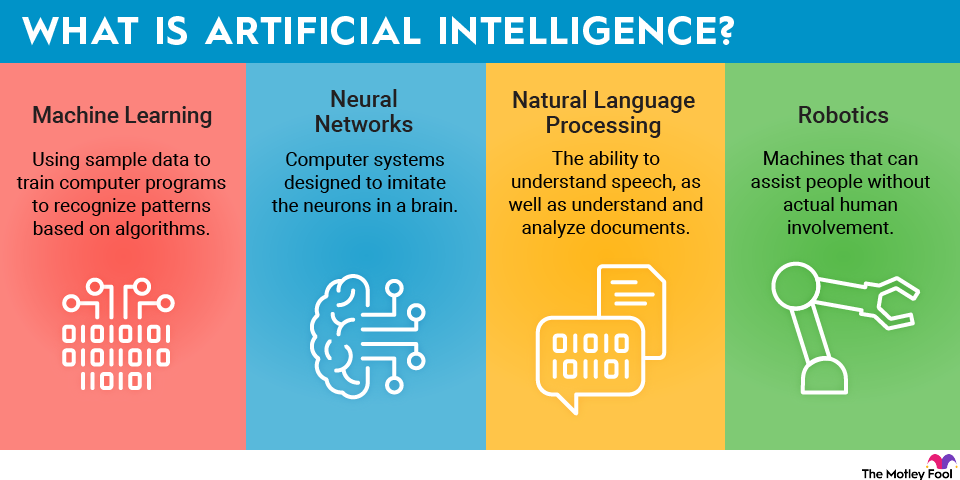
AI is a branch of computer science that focuses on building and managing technology that can learn to autonomously make decisions and carry out actions on behalf of humans. It is not a single technology but rather an umbrella term that includes various components such as machine learning, expert systems, generative AI, and robotics.
AI Components
Today, AI predominantly operates on conventional CMOS-based hardware and combines traditional algorithms with data-driven machine learning models. However, there is growing interest in neuromorphic engineering, which aims to emulate the human brain’s architecture using specialized hardware and algorithms optimized for low power consumption and real-time processing.
AI Use Cases in Business
AI is being applied to a wide range of functions in both lab and commercial/consumer settings. Let’s explore some of the key technologies that are transforming businesses:
Artificial Neural Networks
Artificial Neural Networks are computational models inspired by the structure and functioning of the human brain. They consist of interconnected nodes (neurons) that process and transmit information, enabling the network to learn patterns and relationships from data through training.
Deep Learning
Deep learning is an iterative approach to AI that stacks machine learning algorithms in a hierarchy of increasing complexity and abstraction. It is currently the most sophisticated AI architecture in use today.
Speech Recognition
Speech recognition allows an intelligent system to convert human speech into text or code, enabling seamless interactions between humans and computers.
Natural Language Generation
Natural Language Generation enables conversational interaction between humans and computers, facilitating the generation of human-like text or speech.
Computer Vision
Computer Vision enables machines to analyze and interpret visual information, allowing them to identify objects and patterns in images.
Expert Systems
Expert systems were one of the early AI technologies developed in the 1970s and 1980s. These systems aimed to capture the knowledge and decision-making processes of human experts in specific domains and provide recommendations or make decisions based on that knowledge.
While expert systems may not be as widely discussed as more recent AI technologies, they still have practical applications in healthcare, finance, and engineering.
Exploring the Types of AI

AI can be classified into different types based on its capabilities. Let’s delve into the various categories of AI:
Narrow (Weak) AI
Narrow AI refers to AI systems that are capable of performing only a limited set of predetermined functions. These systems excel at specific tasks but lack the ability to generalize beyond their programmed capabilities.
General (Strong) AI
General AI, on the other hand, aims to equal the human mind’s ability to function autonomously according to a wide range of stimuli. It possesses the capability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across various domains.
Super AI
Super AI is a theoretical concept that envisions AI systems surpassing human intelligence and potentially taking over the world. While this type of AI remains speculative, it sparks discussions about the future implications of AI.
Categorizing AI Initiatives
AI initiatives can also be categorized based on their belonging to one of four categories:
Reactive AI
Reactive AI relies solely on real-time data to make decisions. It does not possess memory or the ability to consider past experiences.
Limited Memory AI
Limited Memory AI, as the name suggests, draws on stored data to make decisions. It can learn from historical information and use it to inform its future actions.
Theory of Mind AI
Theory of Mind AI goes beyond the objective data and considers subjective elements, such as user intent, when making decisions. This type of AI can interpret and respond to human behavior in a more nuanced manner.
Self-Aware AI
Self-Aware AI possesses a human-like consciousness and can independently set goals and use data to decide the best way to achieve those objectives. This type of AI balances its own internal state with external information to make informed decisions.
To better understand these distinctions, let’s compare AI to a professional poker player. A reactive player only considers the current hand in play, while a limited memory player takes into account past decisions made by themselves and other players. A Theory of Mind player factors in behavioral cues from other players. Finally, a self-aware professional AI player stops to consider if playing poker to make a living is truly the best use of their time and effort.
AI vs. Machine Learning
While AI and machine learning (ML) are related, they are not synonymous. Machine learning is a subset of AI that focuses on building models that allow computers to learn from data. ML models use data to make predictions or decisions instead of being explicitly programmed for a task.
It is important to note that while all ML is AI, not all AI involves machine learning techniques. Some AI technologies, such as rule-based expert systems and symbolic AI, fall under the AI umbrella but do not necessarily involve learning from data in the same way ML does.
The Evolving Stages of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence can either replace an entire system or enhance specific processes. For example, a standard warehouse management system can show current product levels, while an intelligent system can identify shortages, analyze their causes, assess their impact on the overall supply chain, and take steps to rectify the situation.
As AI becomes more prevalent in business applications, there is a growing demand for faster and more energy-efficient information processing. Conventional digital processing hardware is unable to keep up with this demand. To address this, researchers are drawing inspiration from the brain and considering alternative architectures that utilize artificial neurons and synapses to process information with high speed and adaptive learning capabilities in an energy-efficient and scalable manner.
Artificial intelligence is transforming industries and reshaping the future. Its potential is vast, and as technology continues to advance, we can expect AI to play an increasingly significant role in our lives. From speech recognition and natural language generation to computer vision and expert systems, the applications of AI are vast and continue to expand. As we navigate this new era of AI-driven innovation, it is essential to understand the different types of AI, the distinction between AI and machine learning, and the various stages of AI evolution. By harnessing the power of AI, businesses can unlock new possibilities and drive growth in the digital age.