In today’s fast-paced business environment, organizations are constantly striving to optimize their processes to achieve maximum efficiency and productivity. One tool that has gained significant popularity in this regard is Pega PRPC (PegaRULES Process Commander). Introduced in 2013 by Pega, PRPC is a Java-based software framework that acts as the core component in Business Process Management (BPM) solutions. In this article, we will explore the capabilities of Pega PRPC, its significance in optimizing business processes, and the key features that make it a powerful tool for driving growth.
What is Pega PRPC?
Pega PRPC is a comprehensive BPM suite that provides organizations with the tools and capabilities to optimize their business processes. It is equipped with industry-interfacing standards and supports declarative rules and multi-threaded execution. With Pega PRPC, organizations can effectively integrate with other systems such as databases, email servers, and Enterprise Information Systems (EIS). This integration is carried out through connectors, which enable seamless data interchange with applications and standards such as HTML, SOAP, .NET, BPEL, JCA, JMS, JSR168, and JSR 94.
Why Choose Pega PRPC?

Pega PRPC is renowned for its ability to adapt to the rapid changes in business processes dynamically. Unlike traditional software development approaches that require extensive coding, Pega PRPC streamlines and speeds up business processes through its automation capabilities. By consolidating all processes into a single platform, Pega PRPC eliminates the need for manual intervention and significantly improves process execution efficiency. Additionally, it offers built-in documentation capabilities, ensuring that process execution and documentation go hand in hand.
One of the key features of Pega PRPC is its ability to identify and resolve performance issues quickly. Whether it’s delays in processing, submitting work objects, or refreshing screens, Pega PRPC actively monitors business processes and responds promptly to address any performance bottlenecks. This dynamic approach to issue resolution and process improvement is a crucial aspect of Pega PRPC, enabling organizations to achieve continuous improvement in their processes over time.
Business Rules in PRPC
Business rules are the brain of any organization, encompassing processes, procedures, practices, policies, constraints, and reasoning capabilities. They reflect the goals of a business in the form of constraints and decisions. Setting business rules is crucial as they determine the outcome of a business. Business logic, which consists of a sequence of operations based on these rules, supports the integration, monitoring, and execution of business processes to achieve optimal results.
To effectively manage and update business rules, Pega PRPC provides a Business Rule Engine (BRE). The BRE is a core Java-based rule engine that facilitates declarative “on-change” processing. It serves as a repository for storing and updating business rules based on changing business needs and regulations. Unlike traditional programming approaches, business rules in Pega PRPC are stored in a non-procedural and non-programming form, making them easily modifiable by non-programmers. The BRE executes business rules separately from other processes in an application, allowing business users to modify rules without affecting other processes. This flexibility enables organizations to streamline operations based on business rules, simplifying complex processes and improving business agility.
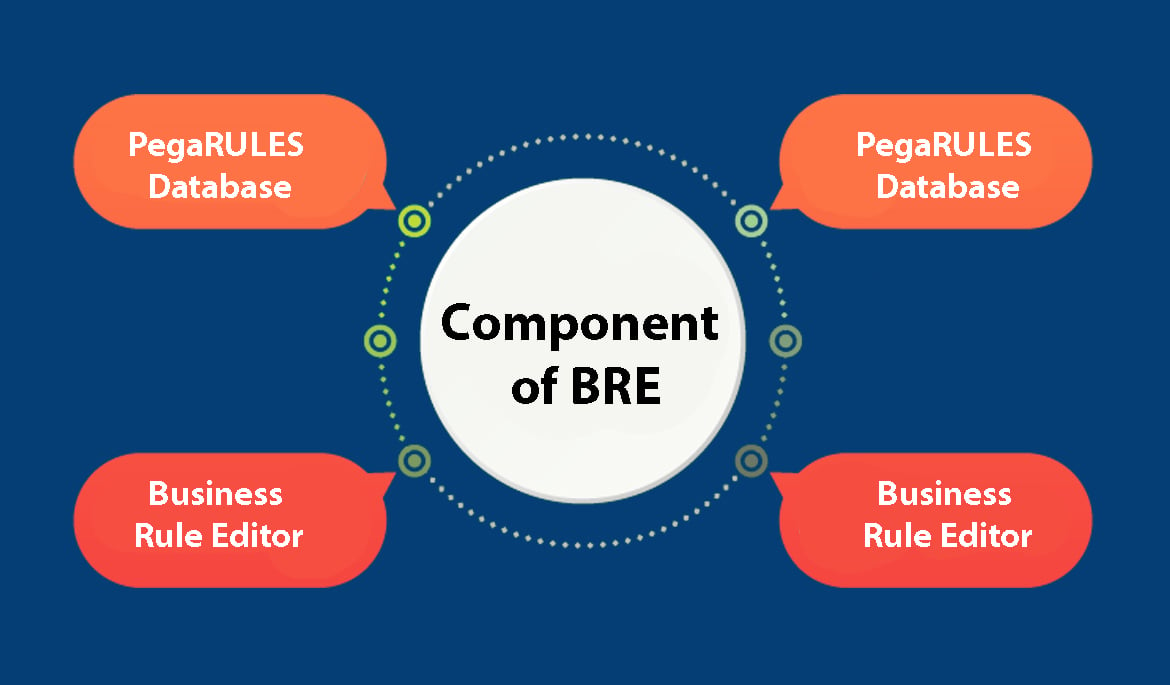
Components of the BRE
The BRE consists of several components that work together to enable effective business rule management. These components include:
-
PegaRULES Database: The PegaRULES database serves as a repository for storing business rules, system information, and related transactions. It provides a centralized location for managing and accessing business rules.
-
Business Rule Editor: The Business Rule Editor is a user interface that allows users to define, edit, and document business rules. It provides a visual representation of the structure of rules and how they will be processed. Users can easily modify rules, delete sets of rules, change the order of rules, and reset the destination of a rule.
-
Reporting Component: The reporting component provides an interface for querying and reporting existing business rules. Users can generate reports on the status and performance of rules.
-
Rule Engine Execution Core: The Rule Engine Execution Core is the programming code responsible for enforcing business rules. It ensures that rules are executed correctly and consistently.
Key Capabilities of Pega PRPC
Pega PRPC offers a wide range of capabilities that address the requirements of BPM solutions. These capabilities enable organizations to optimize their processes and achieve business goals effectively. Let’s explore some of the key capabilities of Pega PRPC:
-
Holistic Modelling and Automation: Pega PRPC allows organizations to create holistic models of their business processes, including properties, process flows, methods, decision rules, expressions, service levels, user interfaces, and event rules. This comprehensive approach to modeling enables organizations to capture all aspects of their processes and automate them efficiently.
-
Business Logic Types: Pega PRPC supports various logic types, including expressions, triggers, service level agreements, decision rules, and constraints. These logic types enable organizations to define and execute complex business rules based on specific conditions and requirements.
-
Real-time Monitoring and Response: Pega PRPC provides real-time monitoring of process Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and takes proactive actions when deviations occur. This capability enables organizations to address issues promptly and ensure smooth process execution.
-
Interoperability with External Tools: Pega PRPC can seamlessly integrate with external tools and applications. It supports data export through Microsoft Excel and enables data analysis using statistical tools like Minitab. This interoperability enables organizations to leverage their existing tools and systems while benefiting from the capabilities of Pega PRPC.
-
Ease of Specialization: By integrating Six Sigma methodologies with Pega PRPC, organizations can easily modify existing processes and rules based on the analysis results of Six Sigma. This integration enables continuous improvement and optimization of business processes.
-
Ability to Run on Versatile Platforms: Pega PRPC is compatible with various operating systems, including Windows, AIX, and Solaris. It can run on popular application servers such as IBM WebSphere, Apache Tomcat, and BEA WebLogic. Additionally, the business rules defined in Pega PRPC can run on relational databases such as Microsoft SQL, Oracle, and IBM DB2.
-
Support for Complex Processes: Pega PRPC provides advanced features such as worklists, process functions, and reporting functions to support complex business processes. Users can manage activities and prioritize work using service level agreements, ensuring efficient task allocation and execution.
Life Cycle Management of PRPC
Pega PRPC facilitates process management and automation through a six-step life cycle management approach. These steps include:
-
Receiving: PRPC accepts data from multiple sources for performing tasks such as modifying or updating processes. This step sets the stage for process execution.
-
Routing: Intelligent matches and assignments are made based on the requirements of tasks. This step ensures that tasks are assigned to the most appropriate resources.
-
Reporting: Real-time visibility of tasks in progress, tasks completed, and productivity and quality metrics is provided. This step enables organizations to track the status and progress of processes.
-
Researching: Analysis and decision-making are performed by connecting with external resources through connectors. This step allows organizations to gather the necessary information for process execution.
-
Responding: Communication with external systems, such as requesting information or updating status, is carried out. This step ensures effective communication and coordination with external systems.
-
Resolving: Tasks are successfully completed and reported to downstream systems automatically. This final step ensures the completion and closure of tasks within the defined process.
Pega PRPC and Six Sigma
To achieve continuous improvement in business processes, many organizations integrate Pega PRPC with Six Sigma methodologies. Six Sigma is a methodology that focuses on identifying key processes in a business and improving their performance to meet quality goals. By combining the capabilities of Pega PRPC and the analysis-driven approach of Six Sigma, organizations can dynamically optimize their business processes based on changing situations. This integrated approach enhances process monitoring, situation selection, event correlation, specialization, and rule definition and execution. It empowers organizations to drive growth and achieve operational excellence.
Pega PRPC and Visio
Visio is a graphical tool that serves as the front-end of Pega PRPC. It allows users to define, edit, and save processes by communicating with the PegaRULEBase. With Visio, users can quickly create business process diagrams, which act as live diagrams that reflect the flow of automated processes in real-time. Business users can view and modify processes as needed, enabling quick adaptation to changing business needs. This seamless integration between Pega PRPC and Visio accelerates business processes and enhances overall efficiency.
Advantages of Pega PRPC
Pega PRPC offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice for organizations seeking to optimize their business processes:
-
Multi-Dimensional Hierarchical Optimization: Pega PRPC maximizes the optimization of processes, decision rules, expressions, and service levels. Its multi-dimensional hierarchical feature ensures that all aspects of a process are optimized to their full potential.
-
Faster and Cost-Effective: Pega PRPC streamlines processes and reduces the need for manual intervention, resulting in faster and more cost-effective operations. It increases the return on investment for organizations by eliminating inefficiencies and reducing the time and effort required to execute processes.
-
Centralized Business Rule Management: Pega PRPC consolidates all disparate and complex business rules into a single location, simplifying rule management and ensuring consistency across processes. This centralized approach improves efficiency and reduces the risk of errors and data redundancy.
-
Adaptability to Business Changes: Pega PRPC is designed to adapt quickly to changes in business requirements. It enables organizations to modify processes and rules in real-time, ensuring that they remain aligned with evolving business needs.
-
Simplification of Complex Business Activities: Pega PRPC provides a comprehensive set of tools and features that simplify complex business activities. It enables organizations to manage activities, prioritize work, and allocate tasks efficiently, resulting in increased productivity and streamlined operations.
-
Enhanced Security: Pega PRPC ensures the security of resources by implementing robust security measures. It protects sensitive data and ensures that only authorized users have access to critical information.
Essential Skills for a PRPC Developer

To become a skilled PRPC Developer, individuals must possess a combination of technical and domain-specific skills. Some of the essential skills required to excel in Pega PRPC development include:
-
Expertise in Pega PRPC: A deep understanding of Pega PRPC versions 5.x, 6.x, and 7.x is crucial for effectively developing and implementing BPM solutions.
-
Knowledge of Programming Languages: Proficiency in Java, J2EE, C++, JSP, EJB, XML, and HTML is essential for leveraging the full capabilities of Pega PRPC.
-
Familiarity with Web Technologies: Familiarity with web technologies such as AngularJS, Java, and JQuery is beneficial for developing user interfaces and integrating external systems.
-
Agile Methodologies: Proficiency in Agile methodologies enables developers to work efficiently in fast-paced development environments and deliver high-quality solutions.
Conclusion
Pega PRPC is a powerful tool that empowers organizations to optimize their business processes and drive growth. With its comprehensive BPM suite and advanced features, Pega PRPC enables organizations to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and achieve operational excellence. By integrating Pega PRPC with methodologies such as Six Sigma, organizations can continuously improve their processes and meet quality goals. With its adaptability, ease of use, and extensive capabilities, Pega PRPC proves to be an invaluable asset in today’s competitive business landscape.