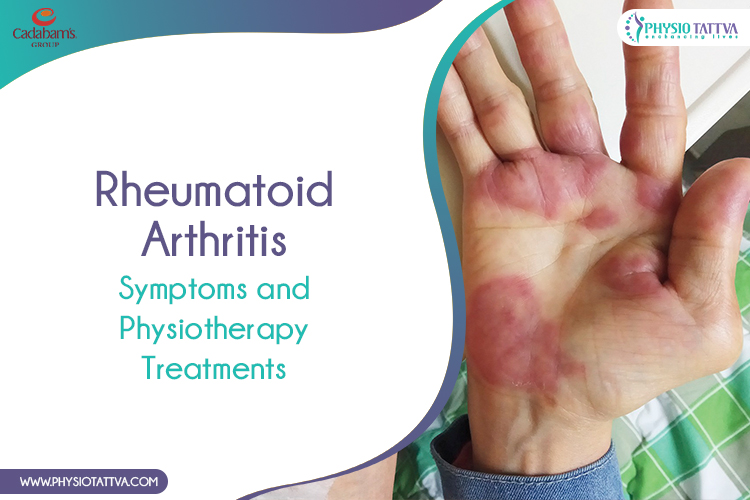
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the joints, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness. If left untreated, RA can cause long-term joint damage and disability. However, with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, it is possible to manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals living with this condition.
Understanding the Goals of Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis
The primary goal of treating rheumatoid arthritis is to reduce joint pain and swelling, which can help maintain or improve joint function. By controlling joint inflammation, individuals with RA can experience a significant reduction in pain and an improvement in their overall quality of life. Additionally, the long-term goal of treatment is to slow or even stop joint damage from progressing.
The Importance of Early Treatment

It is crucial to seek medical attention as soon as symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis are noticed, as joint damage often occurs within the first two years of diagnosis. This early phase is often referred to as the “window of opportunity” and taking advantage of it can help prevent long-term consequences of the disease. Prompt treatment during this period can significantly improve the long-term outcome for individuals with RA.
Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis
The treatment of rheumatoid arthritis involves a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, therapies, medications, and in some cases, surgery. The choice of treatment depends on various factors such as age, overall health, medical history, and the severity of symptoms.
Medications for Rheumatoid Arthritis
There are several medications available to manage the symptoms and slow down the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. The most commonly used medications include:
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These drugs, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, help reduce pain and inflammation in the joints.
-
COX-2 inhibitors: Another type of NSAID, COX-2 inhibitors like celecoxib, have fewer side effects on the stomach and can provide relief from pain and inflammation.
-
Corticosteroids: These medications, including prednisone and cortisone, are effective in reducing pain and inflammation in the joints.
-
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): Unlike NSAIDs, DMARDs can slow down the progression of the disease by modifying the immune system. Commonly prescribed DMARDs include methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, sulfasalazine, and leflunomide.
-
Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors: JAK inhibitors, such as tofacitinib and baricitinib, are another type of DMARD that may be prescribed when methotrexate alone is not effective.
-
Biologics: Biologic response modifiers, also known as biologics, target specific molecules involved in the inflammation process. These medications, including etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, and rituximab, can be highly effective in managing RA symptoms.
It is important to note that the choice of medication will depend on individual factors and the severity of the condition. Regular monitoring and follow-up with healthcare providers are essential to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment and to manage any potential side effects.
The Safest Approach to Rheumatoid Arthritis Medication
The safety of rheumatoid arthritis medication is a significant concern for both healthcare providers and individuals with RA. The safest drug for rheumatoid arthritis is one that offers the most benefit with the least amount of side effects, taking into consideration the individual’s health history and the severity of their symptoms. It is essential to have regular check-ups with healthcare providers to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and address any concerns or side effects.
The Role of Diet and Lifestyle Changes

While changes in diet alone cannot cure rheumatoid arthritis, they can complement the recommended treatments and medications to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms. Incorporating certain dietary changes, such as increasing intake of good fats and reducing consumption of bad fats, salt, and processed carbohydrates, may help manage RA symptoms. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider or nutritionist to ensure that dietary changes are safe and suitable for individual needs.
Maintaining a healthy weight is also important for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, as excess weight puts additional stress on inflamed joints. Weight loss, if necessary, can help reduce joint pain and improve mobility.
Surgical Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis
In some cases, when joint damage is severe and pain is not adequately controlled with medication, surgery may be considered. Surgical interventions aim to restore function to damaged joints and may include procedures such as knee or hip replacements or other surgeries to correct deformities.
Conclusion
Living with rheumatoid arthritis can be challenging, but with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Treatment goals include reducing joint pain and swelling, slowing down joint damage, and maintaining or improving joint function. Medications, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, surgery are all part of a comprehensive treatment plan. By working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with rheumatoid arthritis can find the most suitable treatment options and achieve better control over their condition.